How to calculate volt drop
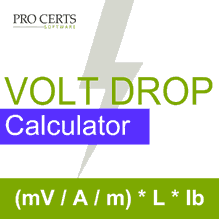
To calculate the voltage drop, use the formula VD = (mV/A/m) x Ib x L ÷ 1000.
Where VD is the total Voltage Drop, mV/A/m is the milliVolt per Amp per meter voltage drop (loss) for a specific cable type and size combination, Ib is the design current in Amps, L is the length of the circuit/cable in meters.
- Enter the load value in Amps.
- Enter the supply voltage.
- Enter the cable length.
- Select a cable type.
- Select the phase (single phase / three phase).
- Calculate
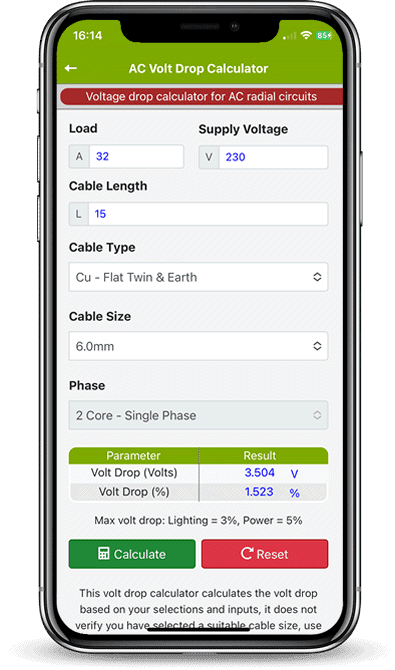
Voltage drop calculation working example
- Load (Ib) = 32 Amps.
- Supply voltage (V) = 230V.
- Cable length (m) = 15 meters.
- Cable type = Flat twin and earth.
- Cable size = 6.0mm².
- mV/A/m = 7.3.
- Calculation VD = 7.3 (mV/A/m) x 32 (Amps) x 15 (meters) / 1000 = 3.5
- Result = 3.5 Volts.
A Flat Twin & Earth 6.0mm² volt drop (mV/A/m) = 7.3, so 7.3 x 32 Amps x 15 meters / 1000 = 3.5 volts.
Online Volt Drop Calculator
Give this free online voltage drop calculator a go, or download the app.
Volt Drop Regulations
525.1 – In the absence of any other consideration, under normal service conditions the voltage at the terminals of any fixed current-using equipment shall be greater than the lower limit corresponding to the product standard relevant to that equipment.
525.201 – Where fixed equipment current-using equipment is not subject of a product standard the voltage at the terminals shall be such as not to impair the safe functioning of that equipment.
525.202 – The above requirements are deemed to be satisfied if the voltage drop between the origin of the installation (usually the supply terminals) and a socket-outlet or the terminals of fixed current-using equipment does not exceed that stated in Appendix 4, section 6.4.
Source: BS 7671