SWA Current Carrying Capacity
The current carrying capacity of an SWA cable will depend on the installation method adopted and the application of any relevant correction factors such as grouping or soil resistivity as a couple of examples.
The easiest way to calculate SWA cables is by using our SWA Cable Calculator.
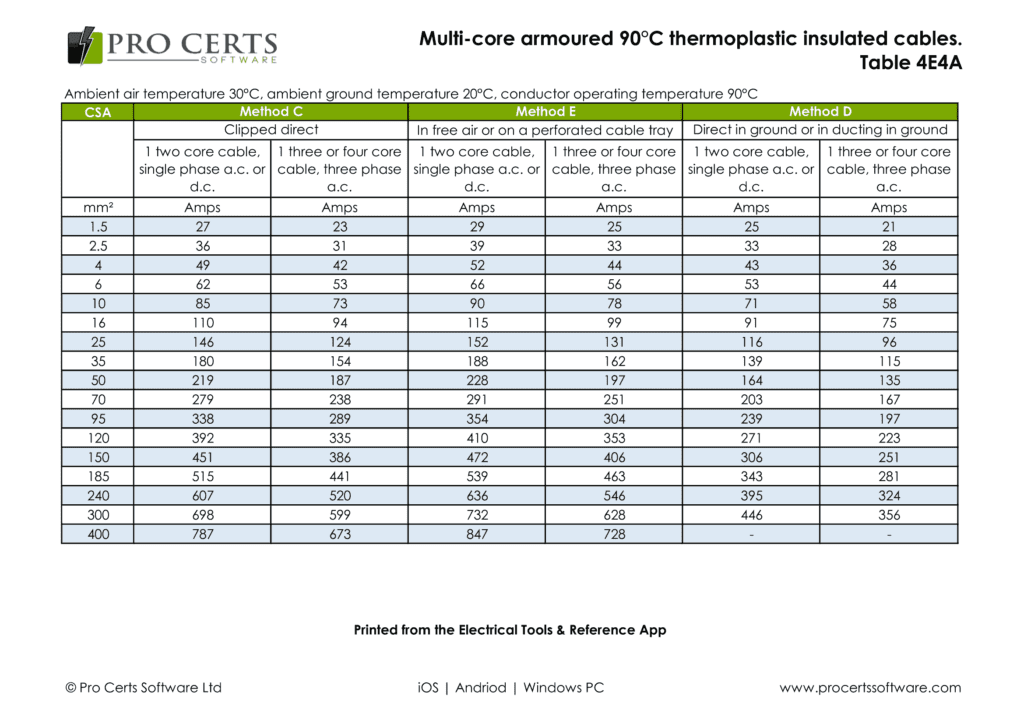
SWA Current Carrying Capacity Tables
SWA current carrying capacity tables are listed in BS 7671, also rating factor tables for various installation methods are listed in Appendix 4 Current Carrying Capacity and Voltage Drop for Cables.
|
CSA |
SWA Clipped Direct Current Carrying Capacity (A) |
|---|---|
|
1.5 mm² |
23 Amps |
|
2.5 mm² |
31 Amps |
|
4 mm² |
42 Amps |
|
6 mm² |
53 Amps |
|
10 mm² |
73 Amps |
|
16 mm² |
94 Amps |
|
25 mm² |
124 Amps |
|
35 mm² |
154 Amps |
|
50 mm² |
187 Amps |
|
70 mm² |
238 Amps |
|
95 mm² |
289 Amps |
|
120 mm² |
335 Amps |
|
150 mm² |
386 Amps |
|
185 mm² |
441 Amps |
|
240 mm² |
520 Amps |
|
300 mm² |
599 Amps |
|
400 mm² |
787 Amps |
SWA current carrying capacity tables include:
- Single-core armoured 70°C thermoplastic insulated cables (non-magnetic armour)
- Multi-core armoured 70°C thermoplastic insulated cables
- Single-core armoured 90°C thermosetting insulated cables (non-magnetic armour)
- Multi-core armoured 90°C thermosetting insulated cables
Cable Calculation Software
- Enter your design parameters.
- Select an installation method.
- Apply correction factors.
SWA Cable Size Current Carrying Capacity
The ccc (current carrying capacity) of an SWA cable is the maximum amount of current the cable can withstand without melting or being subject to damage in normal service.
The maximum current carrying capacity of an SWA cable will depend on many factors, including cable size, number of cores, single phase or three phase and installation reference method.
SWA cables are available in a multitude of sizes and cores varying from 1.5 mm² up to 400 mm² and above. Calculate the required size of an SWA cable which includes current carrying capacity, voltage drop and correction factors.
SWA Cable Size Calculator
Failure to carry out a full and proper SWA cable size calculation may result in an undersized SWA cable being selected, for this, try out our Cable Calculator mobile app.
To calculate voltage drop on its own try the voltage drop calculator.
When selecting an SWA cable size, in addition to checking the current carrying capacity of the SWA cable it is also important to check the voltage drop, maximum permissible Zs value of your protective device and apply any relevant correction factors.
Download The App!
Cable Calc, calculate cable size, voltage drop, R1+R2 and Zs.
For further information visit Cable Calc.
Or, get the cloud desktop version →